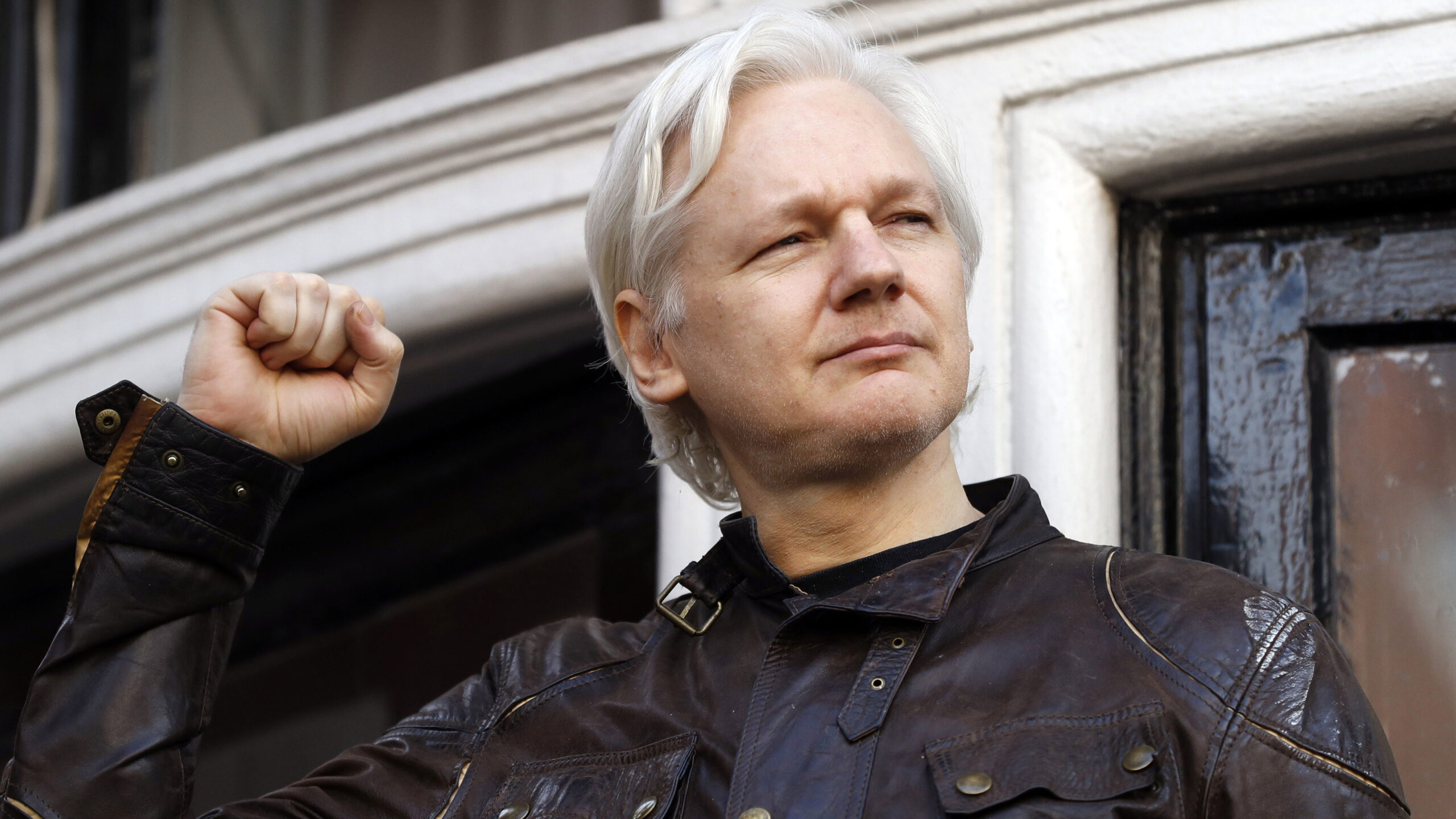
Julian Assange was released from Belmarsh prison on June 24, 2024, after over five years without charges. A prominent figure in whistleblowing and transparency, Assange founded WikiLeaks, which exposed vital truths and questionable actions by powerful entities. His recent plea deal highlights the dangers facing journalism, but his release signals hope for press freedom globally.
Author: Margarida Veríssimo
On Monday, June 24th, 2024, Julian Assange was freed from a maximum-security prison in Belmarsh, England, where he had been held for over five years without ever having been charged with a crime in a UK court.
Assange is a hacker who worked with Anonymous but is known as the creator of the website WikiLeaks, where millions of documents leaked by whistleblowers are published. WikiLeaks first came to fame in the 2000s after exposing its first leaks, and Assange began his reign of exposing all documents of journalistic interest, all that contributed towards truth! So here is a little timeline:
2008
On January 14th, 2008, WikiLeaks released 70 reports considered confidential from the UN that showed ongoing investigations from sexual abuse of refugee girls by UN peacekeepers, to money laundering. These cases of sexual abuse ranged from UN missions in Kosovo to Peru and went unpunished, and in many cases were not properly investigated. Moreover, WikiLeaks revealed that the UN had investigations on the trafficking of weapons, thefts, conflicts of interest, bribes, kickbacks, and fraud, of which many involved blue helmets.
2010
On April 5th, 2010, WikiLeaks released the Collateral Murder video. This video depicts a US helicopter actively killing over a dozen people, including news reporters from Reuters, in a suburb of Baghdad. In the video, it is clear that the attack was unprovoked and children were wounded. Reuters had previously tried to obtain the video but the US had denied access, saying it had analyzed the situation and it was according to “Rules of Engagement”. This video shocked the world and put WikiLeaks in focus throughout all mainstream media.
This video would be followed by the Afghan and Iraq War Logs, released in July and October of that year respectively, which described the lethal and disproportionate use of force as well as unreported killings of Afghan civilians either by NATO or the Taliban. The documents covered a period from 2004 to 2009, and the content was verified and cross-referenced by The Guardian and The New York Times. The Iraq War Logs showed more than 109,000 violent deaths between 2004 and 2009, including 66,000 civilians, which the US had claimed not to keep records of. Torture against Iraqis was also disclosed among other terrible acts. In general, these logs came to show the true face of the War on Terrorism and the silent cost it had so far.
2011
One year later, WikiLeaks, along with NYT, The Guardian, and others, would hit the news again after the release of the Guantanamo files, also known as Gitmo files, which showed the detention of more than 150 innocent Afghans and Pakistanis without charges.
The youngest detainee of the infamous Guantanamo Prison was 14 years old; reasons for imprisonment were non-existent; torture was common; refusals to treat detainees who suffered from depression and other mental health conditions were usual; it was a torture base. This leak once again struck the world and once again the world came to realize the dark alter-ego of US foreign policy.
2012
From there on WikiLeaks would publish documents relating to the involvement of the CIA in the French elections in 2012; emails of several figures of importance; and incriminating documents of several companies, all in the name of political, historical, and social truth and pertinence. By this time Assange is under political attack. In Sweden an alleged case of sexual abuse emerges; Sweden requests the extradition of Assange from the UK; in June Assange begins his battle as he enters the Ecuadorian embassy that provides him political asylum.
2017
In 2017, WikiLeaks released a series of leaks named Vault 7: CIA Hacking Tools. This package released confidential documents from CIA agencies in a total of 24 publications. Malware or hacking tools were discovered to exist in the CIA’s arsenal for surveillance.
These malware were detailed in several documents: Weeping Angels creating a “Fake-off Mode” in Samsung TVs; Grasshoppers infecting Windows; among others;
Moreover, Vault 7 exposed that the CIA ran a dissimulated hacking base in Frankfurt.
Not stopping there in 2018 WikiLeaks released confidential requests from US embassies as well as other leaks.
2019
But some suspect that after leaking the CIA files, pressure started to mount; culminating in 2019, when Trump’s Administration, started pursuing Assange avidly asking for his extradition. In 2019 for what is believed to have been US pressure, Ecuador retracted Assange’s asylum, handing him over to UK authorities; leading to his incarceration; charges for such arrest? None.
Moreover, Assange is an Australian national, making all legal proceedings more intriguing and less just.
Arrested in Belmarsh, a maximum security prison in solitary confinement, Assange, a man who sat at a computer and leaked documents, was now a prisoner of a compound where mass murderers and violent offender paid for their crimes.
2020
In 2020, the hearing begins for Assange’s extradition to the US. What are the charges the US has against him? What is the American legal case? A Virginia court was responsible for this case, which focused mainly on events of 2010, meaning the Iraq and Afghan leaks.
The Afghan and Iraq documents were obtained by Bradley Manning, a US army official and intel analyst, and then sent to Assange, that published them in Wikileaks. In 2010, Bradley Manning was tried in a military court, and sentenced to seven years in prison. To reiterate, there is no proof that Assange hacked the US government. Wikileaks works as a website where documents can be safely published while keeping whistleblowers protected by anonymity. So Wikileaks is not responsible for getting documents but yes providing space for them to be published, just like a newspaper.
Returning to the case, Assange was alleged to have broken US law eighteen times some related to hacking, meaning that Assange, allegedly, helped Manning crack a password from a US government computer. To be reminded he isn’t even charged with cracking the password, but trying. And trying to break the password would break a law on computer fraud from the 1980s. (You will see the trend to use outdated laws in this case) Even if proven true the maximum penalty for this crime, would be five years but knowing that Assange is looking at 175 in a US prison something key is missing.
Well, those 17 other penalties are the result of allegedly breaking the Espionage Act of 1917. More than a century ago during WWI, the US wrote a set laws with the intent to prosecute government officials who spied for other nations, like Manning for example. However, they claim that since Assange helped Manning, and helped in the sense of promising to publish the documents, he is also liable for the same crimes. Meaning that the logic here is “If you helped out, you did it too”. Plus other 3 accounts focus on the fact that the publishing of documents itself is illegal. And so, roughly 170 years are added to the sentence.
And you can re-read that paragraph. Yes, a non-American citizen is being attacked by publishing documents that he didn’t actively get but simply published. This is the end of journalism it would seem. Any journalist, or activist that publishes information once upon a time, confidential, even if relevant, can be punished, through this twisted logic, to life in prison in the US.
2024
And, recently, Assange had made his last appeal against being extradited to the US. It was a somber time, as many expected the appeal to fail, and for Assange to be extradited, and never see the light of the sun again, especially because even in Britain Assange was being treated poorly, and almost inhumanly, having his mental health deteriorating, and him being in severe depression.
Fortunately, this all changed. On Monday 24th June 2024, Assange was released, boarded a plane to Australia, and is now a freeman. Even though he had to make a deal, and had to plead guilty to one account of espionage. But as written by Wikileaks on X (formerly known as Twitter ) “Julian Assange is free, he left Belmarsh maximum security prison on the morning of 24 June, after having spent 1901 days there.”
The plea deal, however puts journalism in a dangerous path. Because Assange had to plea guilty to conspiracy to obtain and disclose national defense information. This means that the US successfully criminalized journalism through this twisted logic we previously discussed “You helped, you did it too”. Moreover extend the jurisdiction of US law, to global citizens. Of course, Assange had to take the deal. His life was at risk in Belmarsh, but this wasn’t an absolute win for journalism.
Even though journalism is still in a perilous state, we now can see the light at the end of the tunnel. And take Julian Assange as a symbol of freedom of the press, and as an impressive individual who showed us the truth, at the cost of over a decade of his life!
Cover Image by: Nine News Australia